About J-ORBIT
The Japan Obesity Research Based on electronIc healTh Records (J-ORBIT) is a comprehensive obesity database directly linked to electronic medical records (EMRs). J-ORBIT is designed to collect structured clinical data efficiently from routine medical practice to clarify the relationship between obesity severity and associated health disorders, thereby contributing to improved treatment and prevention strategies.
Obesity is known to cause various health disorders, such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and more. The Japan Society for the Study of Obesity (JASSO) defines "obesity disease" as obesity accompanied by or with a risk of health disorders, which necessitates medical intervention. However, comprehensive real-world data linking obesity severity and related disorders in clinical practice have been limited.
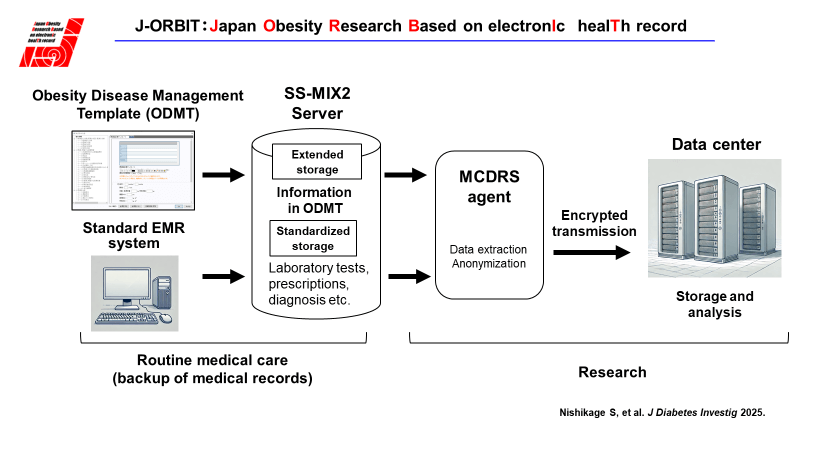
To address this, our team at the Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, led by Professor Wataru Ogawa, developed the J-ORBIT system. This system utilizes the Standardized Structured Medical Information eXchange 2 (SS-MIX2), an electronic medical record storage system established by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, already widely used for electronic health record management in hospitals nationwide. J-ORBIT employs a standardized Obesity Disease Management Template integrated into EMRs, enabling structured and accurate data collection during routine medical care. Collected data, anonymized and securely managed, facilitate large-scale epidemiological analyses to better understand obesity and related health disorders.
Information Disclosure Document
For Patients
Importance of the Research
In Japan, the proportion of adults aged 20 or older classified as obese (BMI ≥25 kg/m²) reached 31.3% in men and 20.6% in women, according to the 2016 National Health and Nutrition Survey. The number of obese men, in particular, has doubled over the past 50 years. Obesity is known to cause a wide range of health issues, including metabolic disorders such as diabetes and dyslipidemia, sleep apnea syndrome, bone and joint disorders, and menstrual abnormalities.
In 2000, the Japan Society for the Study of Obesity (JASSO) established diagnostic criteria for obesity and defined "Obesity Disease" as "a condition characterized by existing or anticipated health disorders caused by or associated with obesity." Clearly identifying individuals who medically require weight loss intervention will enable effective use of healthcare resources, contributing significantly to the prevention of disease onset and progression, and ultimately enhancing healthy life expectancy, which is a major healthcare goal in Japan.
Currently, treatment for obesity disease primarily involves weight reduction through dietary and exercise therapies. Recently, however, medications specifically targeting obesity are being developed, and weight-loss surgery is becoming increasingly popular.
Despite these developments, detailed information about the actual clinical management of patients with obesity disease remains limited. To improve the quality of obesity treatment in Japan, it is essential to collect and analyze patient data systematically through large-scale databases.
Overview of the System
"SS-MIX2" is a standardized electronic medical record information storage system developed and maintained by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. SS-MIX2 is already installed in major hospitals nationwide, including university hospitals.
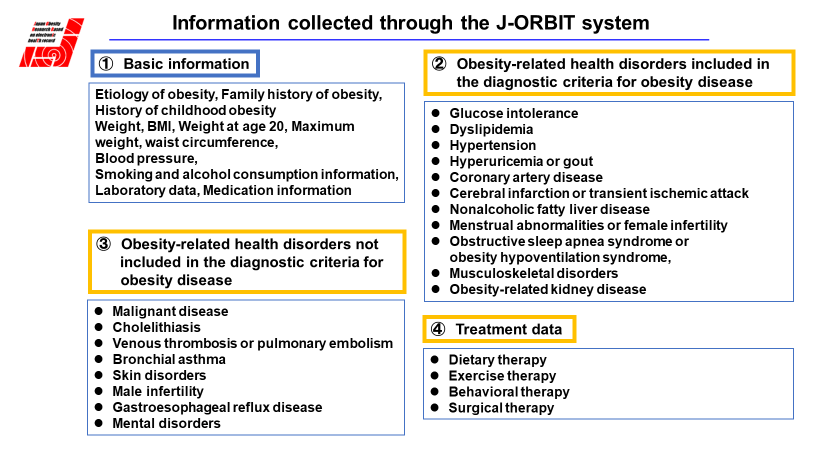
SS-MIX2 enables uniform data collection across hospitals, regardless of variations among electronic medical record vendors. Participating medical institutions introduce a specialized electronic medical record data-entry interface known as the "Obesity Disease Management Template." Physicians use this template during clinical consultations with obesity patients, integrating data entry directly into their medical records.
Entered data are anonymized to protect patient privacy and then efficiently stored electronically in a centralized database.